For 30 years of Linux, Linus Torvalds focuses on version 5.14 of the kernel
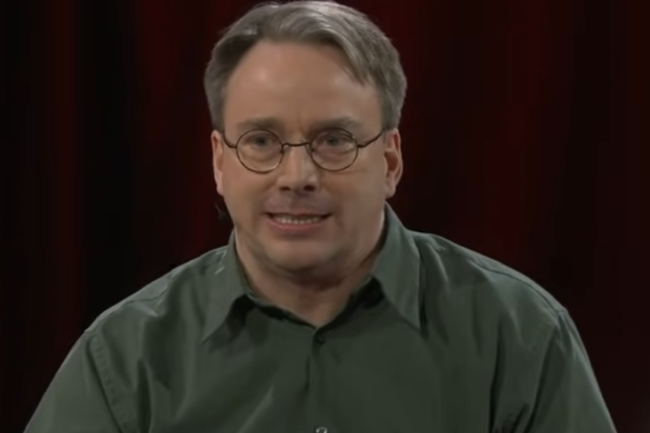

The father of Linux has his own way of celebrating 30 years of the debut of the open source OS. Away from the festivities, Linus Torvalds prefers to focus on the release of the latest version of the kernel, 5.14.
Resolutely taking care of Linux is no longer a mere “hobby” for Linus Torvalds. 30 years ago, however, it was the qualifier of his message relating to the creation of a free OS. Three decades later, the Linux dad has just recalled that despite the festivities, the work on the kernel never stops. In a post, he said “when you are done celebrating 30 years of Linux, try the new Linux 5.14”.
True to himself, he doesn’t hesitate to tackle this abundance of celebrations, “I realize you are all busy with galas, balls and all the other 30th anniversary events, but at some point you must be tired of glitter, fireworks and champagne ”. And to remind the community: “Version 5.14 is here, it is just waiting for you to test it and remind you of the meaning of all these festivities”.
The benefits of Linux 5.14
What are the benefits of the latest iteration of Linux? The most important are arguably memfd_secret and core scheduling, which are a response to the Specter and Meldown flaws affecting Intel chips. Thus, memfd_secret allows applications to create an area of memory that only that application can access, not even the kernel. Also, Linux can now allow hyperthreading more efficiently (one way to mitigate Specter and Meltdown was to disable it) and ensure that reliable or unreliable workloads share a single kernel.
Also on Intel, version 5.14 offers more support for the Alder Lake platform. It also targets the RISC-V architecture by giving it better access to certain essential kernel functions, such as the “transparent hugepages” memory mapping function. In addition, the inclusion of SimpleDRM (Direct Rendering Manager) improves the management of GPUs. Other functions also include adjusting CFS bandwidth control, optimizing resource limitations in user spacenames. There is also a controller for I / O prioritization, as well as support for the PCI-over-virtio driver.